Work Permits in the U.S.
Types of Work Permits for Foreign Nationals
When it comes to foreign nationals seeking employment in the U.S., there are various types of work permits available, catering to different circumstances and needs. Below, we’ll delve into the primary categories of work permits:
Employment Authorization Document (EAD)
- Issued by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
- Allows non-citizens to legally work in the U.S.
- Common for individuals with temporary protected status, asylum seekers, and certain non-immigrant visa holders.
Non-Immigrant Work Visas
These are suitable for those seeking temporary employment in the U.S., typically filed by a potential employer with the USCIS before the individual applies for a visa:
H-1B Visa
- For specialized professions requiring a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- Popular among IT professionals.
L-1 Visa
- For employees being transferred within the same company to a U.S. office.
- Includes executives, managers, and specialized knowledge workers.
O-1 Visa
- For individuals with extraordinary abilities in sciences, arts, education, business, or athletics.
This comprehensive guide provides an overview, ensuring prospective applicants are well-informed about their options for work permits and visas, essential for a legal and organized path to working in the U.S.
Eligibility Criteria for Obtaining a Work Permit
To successfully obtain a work permit, U.S. immigrants must meet certain eligibility criteria. These criteria are designed to ensure that the applicant is legally authorized to hold employment in the United States.
Eligible Immigrants Include:
- Holders of pending green card applications
- Applicants awaiting permanent residency.
- Spouses of certain visa holders
- For instance, spouses of H-1B visa holders.
- Individuals with Temporary Protected Status (TPS) or Deferred Enforced Departure (DED)
- Immigrants from designated countries facing conditions preventing their safe return.
- Approved temporary workers experiencing financial hardship
- Workers facing unexpected financial strain.
- Students applying for Optional Practical Training (OPT)
- Allows F-1 visa students to work in their field of study.
Understanding these criteria is crucial, as it ensures non-citizens can determine their eligibility for work permits, paving the way for legal employment opportunities in the U.S.
Visas for Working in the U.S.
Common Work Visas Available
For foreigners eager to work in the U.S., various work visas cater to different professional needs and circumstances. These temporary non-immigrant visas typically require a sponsoring employer to file a petition with the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
H-1B Visa
- Suitable for professionals in specialty occupations.
- Requires a bachelor’s degree or higher.
L-1 Visa
- For intra-company transferees.
- Covers executives, managers, and specialized knowledge workers.
O-1 Visa
- For individuals with extraordinary abilities.
- Applicable to fields like science, arts, education, business, or athletics.
E-2 Visa
- Available for investors from treaty countries.
- Requires substantial investment in a U.S. business.
TN Visa
- Exclusive to Canadian and Mexican professionals.
- Part of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
H-2B Visa
- For temporary non-agricultural workers.
- Typically seasonal or peak-load employment.
These common work visas enable foreigners to legally reside and work in the United States, fueling the country’s diverse workforce.

Application Process for Work Visas
Understanding the application process for work visas is crucial for securing legal employment in the U.S. After identifying the appropriate visa, applicants must follow specific steps to ensure a successful application.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Fulfill Prequalifying Conditions
- Meet eligibility criteria.
- Secure a job offer from a U.S. employer.
- Sponsorship Petition
- Your employer submits Form I-129 to USCIS.
- Wait for petition approval.
- Gather Required Documents
- Ensure passport validity.
- Collect employer support letter.
- Submit Visa Application
- Complete DS-160 online visa form.
- Pay the visa application fee.
- Schedule Visa Interview
- Visit the U.S. Embassy or Consulate.
- Attend an interview with all necessary documents.
Contact Local US Embassy
- For more specific requirements.
- Obtain personalized guidance.
These steps form the basic framework of the application process, enabling foreign nationals to successfully apply for U.S. work visas and embark on their professional journey in the United States.
Difference Between Work Permits and Work Visas

Key Distinctions Between Work Permits and Work Visas
Understanding the key distinctions between work permits and work visas is essential for those aiming to work internationally. While both are vital, they serve different purposes and have unique requirements.
Work Visas
- Purpose: Authorize entry and stay in the U.S.
- Type: Generally temporary and tied to specific jobs.
- Application: Processed before arrival in the U.S.
Work Permits (EAD)
- Purpose: Authorize individuals to work in the U.S.
- Type: Long-term validity for various employment options.
- Application: Often required alongside a visa.
Key Differences:
Duration
- Visas: Usually for a fixed, shorter period.
- Permits: Valid for longer durations, often renewable.
Scope
- Visas: Tied to specific employers or job types.
- Permits: Offer broader work eligibility across multiple employers.
Interdependence
- A visa is typically needed to enter and stay in the U.S.
- A work permit grants the actual employment authorization.
Navigating these distinctions helps foreigners understand the necessary paperwork, paving the way for a successful and legal employment journey in the United States.

Understanding the Limitations and Benefits of Each
When considering work permits and work visas, it’s crucial to understand the specific limitations and benefits each offers. This knowledge aids in making informed decisions for legal employment in the U.S.
Work Visas
Benefits:
- Job Security: Tied to a specific employer, offering stability.
- Legal Entry and Stay: Authorizes your presence in the U.S.
Limitations:
- Employer Dependency: Limited to the sponsoring employer.
- Temporary Nature: Often restricted to a fixed duration.
Work Permits (EAD)
Benefits:
- Flexibility: Allow working with multiple employers.
- Longevity: Typically valid for longer periods, with renewal options.
Limitations:
- Complex Application Process: Requires meeting specific eligibility criteria.
- Dependency on Visa Status: Often needs to be coupled with a visa for legal stay.
Comparative Benefits:
Visas vs. Permits
- Visas: Essential for legal entry and residency.
- Permits: Critical for employment authorization across employers.
Comparative Limitations:
- Work Visas: Limited by employer and duration.
- Work Permits: Complicated application and dependency on visa status.
Understanding these aspects ensures that foreign workers and employers navigate the work visa and permit landscape effectively, optimizing employment opportunities in the United States.
Requirements for Working in the U.S.

Documents Needed for Working in the U.S.
Before starting employment in the U.S., foreigners must gather essential documents to ensure legal compliance. These documents facilitate authorization and verification processes.
Visa Documentation
- Work Visa (e.g., H-1B, L-1, O-1)
- Confirms legal entry and stay in the U.S.
- Must be approved before applying for a work permit.
Employment Authorization Document (EAD)
- What It Is: Official permit from the U.S. government.
- Purpose: Allows legal employment in any U.S. company.
- Validity: Linked to the duration of your visa.
Required Supporting Documents
- Passport: Validity beyond the intended stay.
- I-94 Arrival/Departure Record: Proof of lawful entry.
- Employer Documents:
- Job offer letter.
- Form I-129 petition approval notice.
Social Security Number (SSN)
- Purpose: Necessary for taxation and payroll.
- Application: Can be done alongside EAD filing.
Other Essential Documents
- Proof of Address: Utility bills or rental agreements.
- Educational Qualifications: Diplomas and certifications.
Having these documents in order ensures a smoother entry into the U.S. workforce, supporting compliance with federal regulations and facilitating a legitimate professional pathway.
Legal Obligations and Rights of Foreign Workers
Understanding the legal obligations and rights of foreign workers in the U.S. is critical for maintaining lawful employment and protecting individual interests. Both employers and employees must familiarize themselves with these regulations.
Legal Obligations
Employment Compliance
- Maintain Valid Visa and EAD:
- Ensure both remain up-to-date.
- Renew before expiration.
Tax Commitments
- Social Security and Medicare:
- Deductions from earnings.
- Contributions by employers and employees.
- Federal and State Taxes:
- File annual tax returns.
- Obtain a Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN).
Rights of Foreign Workers
Worker Protection
- Fair Treatment: Right to work in a non-discriminatory environment.
- Wages and Hours: Entitled to fair wages and reasonable working hours.
Workplace Safety
- Occupational Safety: Employers must ensure safe working conditions.
- Health Benefits: Eligibility for workplace health programs.
Freedom of Association
- Union Membership: Right to join and form unions.
- Collective Bargaining: Engage in negotiations with employers through representation.
Protection and Resources
- Legal Support: Access to legal aid for work-related disputes.
- Government Resources: Pamphlets and information on rights and protections.
By adhering to these obligations and understanding their rights, foreign workers can ensure a fair and secure work environment while supporting their professional endeavors in the United States.
Renewing Work Permits and Visas

Process for Renewing Work Permits and Visas
Renewing work permits and visas ensures ongoing legal employment and residency in the U.S. Navigating this process requires attention to timely documentation and specific procedural steps.
Work Permit Renewal
Eligibility and Timing
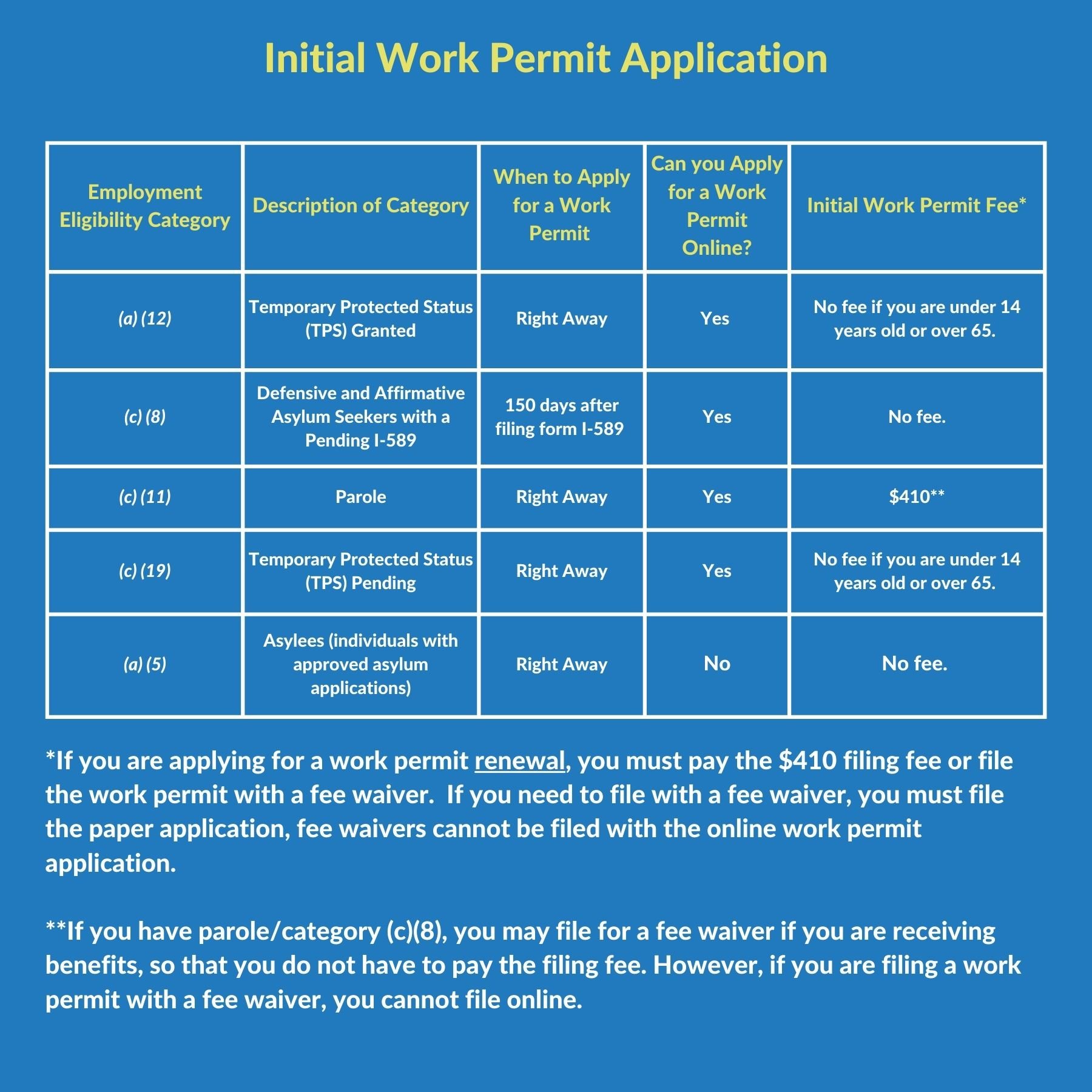
- Renewal Window: Apply 180 days before expiration.
- Eligibility: Must still meet original permit conditions.
Application Steps
- Form I-765 Submission:
- Complete and submit the renewal form.
- Include required documents (passport, current EAD).
- Supporting Documents:
- Copy of original work permit.
- Form I-94 Arrival/Departure Record.
- Two passport-sized photos.
- Biometrics Appointment:
- Attend an appointment if required by USCIS.
Visa Renewal
Application Process
- Pre-conditions: Maintain a valid passport and employment.
- Form DS-160: Complete the required online visa application form.
Steps for Renewal
- Schedule an Interview:
- At the U.S. Embassy or Consulate.
- Bring employment verification and financial documents.
- Pay Application Fees:
- Fees vary based on visa category.
- Attend Visa Interview:
- Provide hard copies of all documents.
- Answer questions regarding continued stay and employment.
Final Approvals
- Await USCIS Decision:
- Approval may take several weeks.
- Check processing times and statuses online.
Understanding these procedures ensures that immigrants can continue their professional journey in the U.S. without interruptions, supporting both temporary and long-term employment goals.
Important Considerations During the Renewal Process
Renewing a work permit (EAD) or visa requires careful attention to detail and adherence to specific guidelines. Ensuring a smooth renewal process involves several key considerations.
Timing and Deadlines
Early Application
- Renewal Window: Apply 180 days before expiration.
- Avoid Gaps: Ensures continuous employment authorization.
Documentation
Required Documents
- Current EAD or Visa
- Submit along with Form I-765 or DS-160.
- Supporting Evidence
- Job offer letter, Form I-94, passport copies.
Application Process
Accurate Completion
- Forms and Fees:
- Correctly complete all necessary forms.
- Pay the required application and biometrics fees.
Legal Requirements
Eligibility Verification
- Maintain Eligibility:
- Ensure you still meet the original visa or work permit conditions.
- Employer Sponsorship:
- Confirm job continuity or new employer’s sponsorship.
USCIS and Consulate Engagement
Follow-ups and Appointments
- Biometrics: Attend any required biometrics appointments.
- Interviews: Be prepared for consulate interviews if renewing visas.
Proactive Measures
- Regularly check the status on USCIS or consulate websites.
- Address any requests for additional information promptly.
By considering these factors, nonimmigrant visa and permit holders can streamline the renewal process, ensuring they remain compliant with U.S. laws and continue their employment seamlessly.
Conclusion

Summary of Work Permits and Visas for Working in the U.S.
Navigating the landscape of work permits and visas in the U.S. is crucial for nonimmigrant professionals and students. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various options available, from temporary labor visas to long-term work permits.
Work Visas
Types of Work Visas
- H-1B: For specialty occupations.
- L-1: For intra-company transferees.
- O-1: For those with extraordinary abilities.
Process and Requirements
- Employer Sponsorship: Essential for visa approval.
- Duration: Often temporary, specific to job roles.
Work Permits (EADs)
Eligibility
- Nonimmigrant Visa Holders: Must obtain EAD for legal employment.
- Permanent Residents: May need an EAD based on status.
Application Process
- Form I-765: Primary application form.
- Supporting Documents: Passport, visa, and employment proof.
Legal Rights and Protections
Employee Protections
- Fair Wages and Hours: Guaranteed by U.S. labor laws.
- Workplace Safety: Employers must ensure safe working conditions.
Renewal and Transition
Renewal Considerations
- Application Timing: Apply 180 days before expiration.
- Continuous Compliance: Maintain eligibility and documentation.
Understanding these elements helps foreign nationals smooth their path to legal employment in the U.S., ensuring they take full advantage of the opportunities while remaining compliant with federal guidelines.
Useful Resources for Further Information
For those seeking to work in the U.S., several valuable resources offer comprehensive guidance. These official websites and publications ensure that prospective employees and employers have access to accurate and up-to-date information.
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS)
- Website: USCIS.gov
- Content: Information on work permits (EADs), visa classifications, and application processes.
- Features: Forms, guides, and processing times.
U.S. Department of State
- Website: Travel.State.Gov
- Content: Detailed visa information, including employment-based nonimmigrant visas.
- Features: Visa application guides, interview scheduling, and embassy contacts.
USAGov
- Website: USA.gov
- Content: Resources for working in the U.S., legal rights, and protections.
- Features: Links to official government services and publications.
Department of Labor (DOL)
- Website: DOL.gov
- Content: Employee rights, workplace safety, and wage information.
- Features: Regulations, compliance guidelines, and support resources.
Immigrant and Refugee Resources
- Community Organizations:
- Provide legal aid and support for navigating the work authorization process.
By leveraging these resources, noncitizens and employers can confidently navigate the complexities of U.S. work permits and visas, ensuring compliance and benefiting from available opportunities.

